Understanding Trophic Cascades in Ecosystems Impact and Dynamics Biology Diagrams When the impact of a predator on its prey's ecology trickles down one more feeding level to affect the density and/or behavior of the prey's prey, ecologists term this interaction a feeding, or

Classic Examples of Trophic Cascades; An Ecosystem-Wide Trophic Cascade: The Wolves of Yellowstone National Park ; Trophic cascades are powerful indirect interactions that can control entire ecosystems, occurring when a trophic level in a food web is suppressed. For example, a top-down cascade will occur if predators are effective enough in predation to reduce the abundance, or alter the

Trophic cascades across ecosystems Biology Diagrams
12 Trophic Cascade Examples To Boost Ecosystem. The concept of trophic cascades refers to the ripple effects that occur in an ecosystem when a change in one species' population has a cascading impact on other species and the environment. This example illustrates how a single species can have a cascading effect on the structure and However, only recently have ecologists explicitly examined how organisms with complex life histories can dynamically couple aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems 15,16,17, leading to trophic cascades
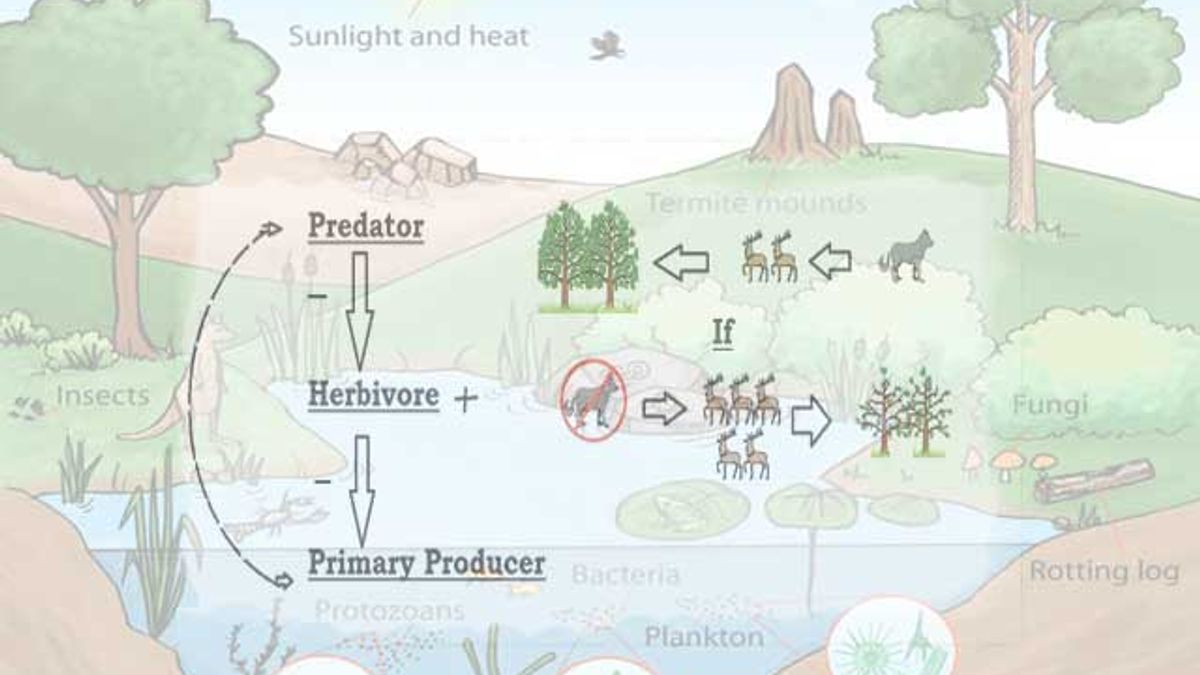
What is Trophic Cascade? A trophic cascade is a side-effect when a trophic level (species) of the ecosystem is reduced or removed. This triggers a cascade (series of events/ effects on other species) that changes the balance of the entire ecosystem. The ecological species interactions keep entire ecosystems balanced.

What is Trophic Cascade? Various Types, Effects and Examples Biology Diagrams
A trophic cascade is a powerful process that occurs in an ecosystem when a change at one level affects multiple other levels.It usually starts when a keystone species - often a top predator - is removed or added to an ecosystem, leading to major shifts in the populations of species at various levels.This ripple effect shows how interconnected every part of a food web is, from the smallest

In many instances, trophic cascades have been initiated by human persecution and harvesting of top carnivores, such as wolves and big cats in terrestrial ecosystems and sharks, tunas, and game fish in aquatic ecosystems.The removal of top carnivores triggers significant effects on prey populations, primary producers, and ecosystem processes. Typically, trophic cascades are considered top-down or bottom-up — and any significant disruption could cause the entire ecosystem to collapse. In a top-down cascade, apex predators that control the lower trophic levels disappear, which alters the food web — not entirely surprising considering humans have driven the extinction rate 1,000 to
